 The energy landscape in the United States is shifting rapidly. Rising utility prices, extreme weather events, and growing datacenter energy consumption concerns are straining an already fragile grid. In 2021, the average U.S. household experienced more than seven hours of power interruptions, with states like Texas averaging over 20 hours due to storms and grid stress (Time, 2022). Homeowners are looking for reliable solutions that go beyond grid dependence or outdated generator-only systems. Solar energy storage and hybrid inverters are devices that integrate solar, energy storage, and grid connectivity. And are emerging as the smartest choice for 2025 and beyond, offering resilience, seamless home backup power, and energy cost savings.
The energy landscape in the United States is shifting rapidly. Rising utility prices, extreme weather events, and growing datacenter energy consumption concerns are straining an already fragile grid. In 2021, the average U.S. household experienced more than seven hours of power interruptions, with states like Texas averaging over 20 hours due to storms and grid stress (Time, 2022). Homeowners are looking for reliable solutions that go beyond grid dependence or outdated generator-only systems. Solar energy storage and hybrid inverters are devices that integrate solar, energy storage, and grid connectivity. And are emerging as the smartest choice for 2025 and beyond, offering resilience, seamless home backup power, and energy cost savings.
The Limitations of Power Grid Dependence
Aging infrastructure and new energy demands are pushing the U.S. grid to its limits. Outages are not only becoming more frequent, but they also take longer to restore, rising by 16% in frequency and 33% in duration over the past decade (SEPA, 2023). Added to this is the explosive growth in artificial intelligence and datacenter development, which significantly increases electricity consumption and further stresses grid reliability (U.S. Department of Energy, 2023). Bottomline: for homeowners depending solely on the grid, it means higher bills and less reliability.
Why Generator-Only Backups Fall Short
Generators have long been seen as the go-to backup for outages, but their drawbacks are becoming harder to ignore. The average cost to install a whole-home generator is about $12,070, with a top-end range up to $19,050 (The Spruce, 2023). On top of that, the ongoing fuel expense is steep: natural gas averages around $0.25 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) and gasoline can cost as much as $0.73 per kWh (Option One Solar, 2023).
Generators also bring added burdens: noise, emissions, regular maintenance, and limited lifespan. In extended outages, they depend on fuel availability, which is often disrupted during storms and disasters. In contrast, solar and storage provide renewable power that replenishes daily.
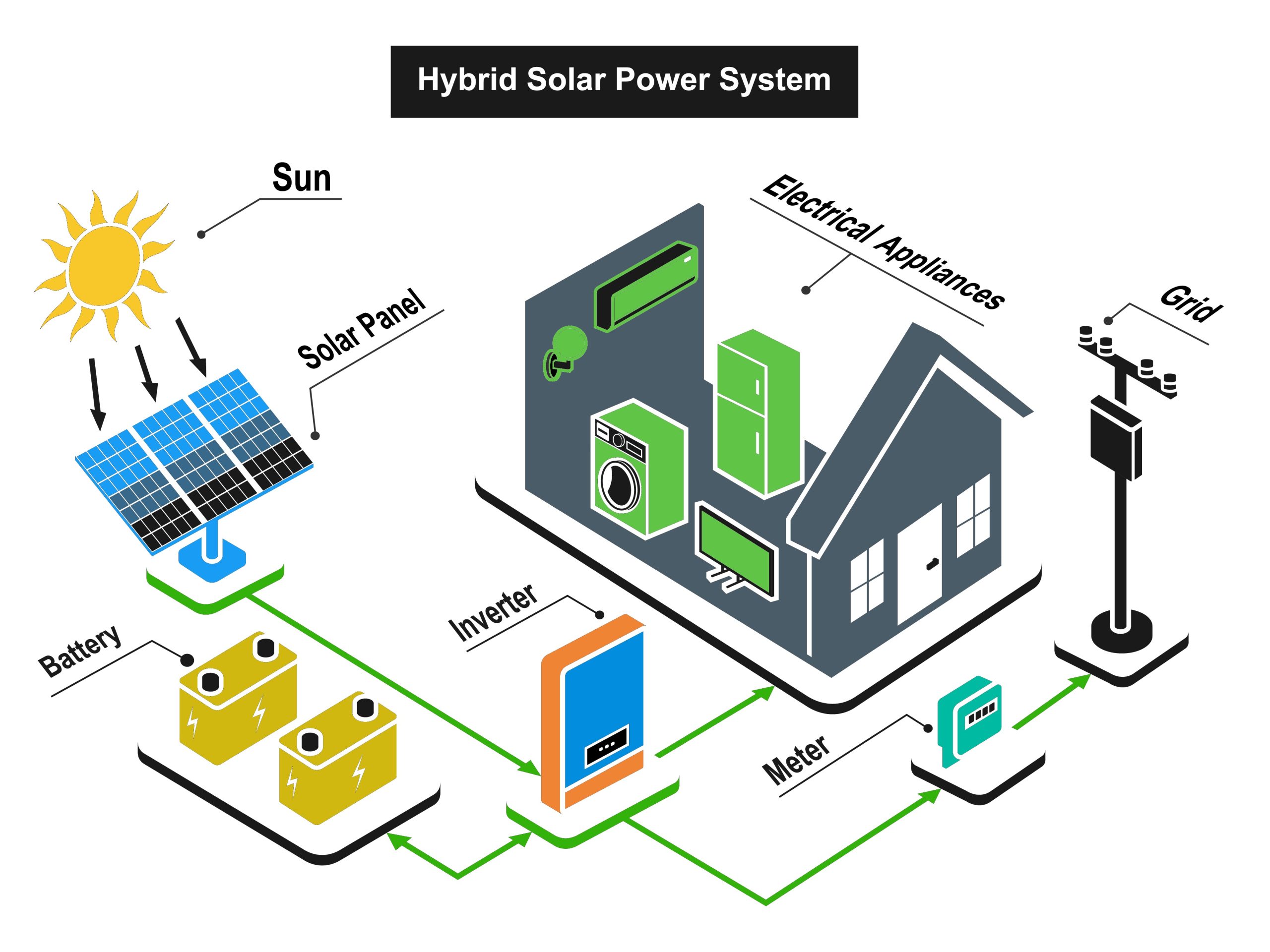
Hybrid Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work
 Hybrid inverters serve as the intelligent hub of a home energy system. They integrate rooftop solar panels, battery storage, the utility grid, and even a backup generator if desired. Their bi-directional power flow allows homeowners to not only consume but also store or export energy.
Hybrid inverters serve as the intelligent hub of a home energy system. They integrate rooftop solar panels, battery storage, the utility grid, and even a backup generator if desired. Their bi-directional power flow allows homeowners to not only consume but also store or export energy.
During normal operation, hybrid inverters prioritize solar usage, store excess energy in batteries, and switch seamlessly between grid and stored power as conditions demand. This flexibility ensures homeowners get the most from their investment, while reducing reliance on external, unstable sources of energy.
Resilience: Home Power When the Grid Goes Down
Hybrid inverters and battery storage systems are designed to keep critical loads running when the grid fails. Air conditioning, refrigeration, lighting, and even medical devices can remain powered thanks to instant switchover capabilities. Research shows that during outages, homes with multiple energy sources – solar, battery, and generator – are up to 93% more reliable. Helping to maintain about 85% of critical household functions compared to fuel-only systems (Batten Emergency, 2023).
With average outage times climbing nationwide, hybrid inverters transform resilience from a luxury into a necessity. Unlike generators that rely on supply chains, hybrid systems draw from renewable energy, reducing vulnerability during extended blackouts.
Cost Savings: Solar Energy Storage Outperforms the Alternatives
Higher Upfront Investment for Long-Term Benefits & ROI
While backup batteries require an upfront investment, their long-term savings quickly outpace generators. A 13.5 kWh home battery costs about $9,400 after incentives, compared to $7,000 for a generator (EnergySage, 2023). Larger battery systems can run between $10,000 and $20,000, but unlike generators, they eliminate ongoing fuel costs and require minimal maintenance (8M Solar, 2024).
The difference becomes stark in multi-day outages. A three-day generator backup can cost about $626 in fuel alone. Over the lifespan of the equipment, this translates to thousands of dollars in savings. Beyond outages, hybrid inverters cut costs by enabling self-consumption of solar, peak shaving with time-of-use programs, and participation in virtual power plants (VPPs) and other initiatives.
2025: Policy, Incentives, and Future-Proofing
Federal incentives remain central to the residential solar energy storage market. The 30% Investment Tax Credit (ITC) chief among them. For homeowners, the requirement is straightforward: energy storage systems must be installed by December 31, 2025, to qualify for the 30% residential tax credit under Section 25D. This creates a tremendous urgency, as waiting too long could mean missing out on major savings.
If everything goes perfectly, no hiccups or hangups in paperwork, permitting, equipment, etc., depending on the size of the system being installed, solar panels (PV), hybrid inverter, and battery storage could be 2 – 5 days. For homeowners and small businesses, this creates a narrow but critical window in 2025 to act. Waiting until after 2025 risks facing higher equipment costs, limited availability of compliant products, and potential installation delays due to supply bottlenecks.
Hybrid inverters remain future-ready and capable of integrating participating in virtual power plants and aligning with evolving utility programs. But the opportunity to secure the maximum financial benefits while avoiding regulatory complications is rapidly closing.
References
Batten Emergency. (2023). Prepare for long-term power outages. Retrieved from https://battenemergency.com/briefs/prepare-for-long-term-power-outages/
Clean Start. (2024). Solar battery vs. gas generator: Which is best for your home? Retrieved from https://www.cleanstartforme.com/solar-battery-vs-gas-generator-which-is-best-for-your-home/
EnergySage. (2023). Battery backup power vs. generators. Retrieved from https://www.energysage.com/energy-storage/battery-backup-power-vs-generators-which-is-right-for-you/
Investopedia. (2023). The economics of solar power. Retrieved from https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/061115/economics-solar-power.asp
Nature. (2025). Rooftop solar and battery viability across U.S. households. Nature Energy. Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-025-01822-9
Option One Solar. (2023). Solar panels vs. generator backup: Cost comparison guide. Retrieved from https://optiononesolar.com/blog/solar-panels-vs-generator-backup-cost-comparison-guide
SEPA. (2023). Resilience via residential solar and storage. Retrieved from https://sepapower.org/knowledge/resilience-via-residential-solar-storage/
The Spruce. (2023). Whole-house generator cost. Retrieved from https://www.thespruce.com/whole-house-generator-cost-8414587
Time. (2022). Extreme weather is making power outages more frequent. Retrieved from https://time.com/6235156/extreme-weather-us-power-outages/
U.S. Department of Energy. (2023). DOE releases report evaluating U.S. grid reliability and security. Retrieved from https://www.energy.gov/articles/department-energy-releases-report-evaluating-us-grid-reliability-and-security
Wikipedia. (2024). Cost of electricity by source. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cost_of_electricity_by_source
8M Solar. (2024). Whole house battery backup vs. generators. Retrieved from https://8msolar.com/whole-house-battery-backup-vs-generators/
